Change Data Capture Using Debezium
One of the popular Change Data Capture (CDC) systems is debezium. In this blog post, we will discuss how to setup debezium and how it works internally
Table of contents
- Introduction
- Use-cases of CDC
- Debezium
- Debezium and MySQL
- Troubleshooting Debezium
- The MySQL server is not configured to use a ROW binlog_format, which is required for this connector to work properly
- Database history topic retention.ms should be ‘-1’ or greater than 5 years
- The connector is trying to read binlog but this is no longer available on the server.
- Could not find the first log file name in the binary log index file Error code: 1236; SQLSTATE: HY000.
- io.debezium.DebeziumException: Failed to read next byte from position 1640249837
- MySQLTransactionRollbackException: Lock wait timeout exceeded; try restarting transaction
Introduction
What is change data capture? A change that occurred in one data source will be captured and replicated in another data source. Let's understand it with a picture.
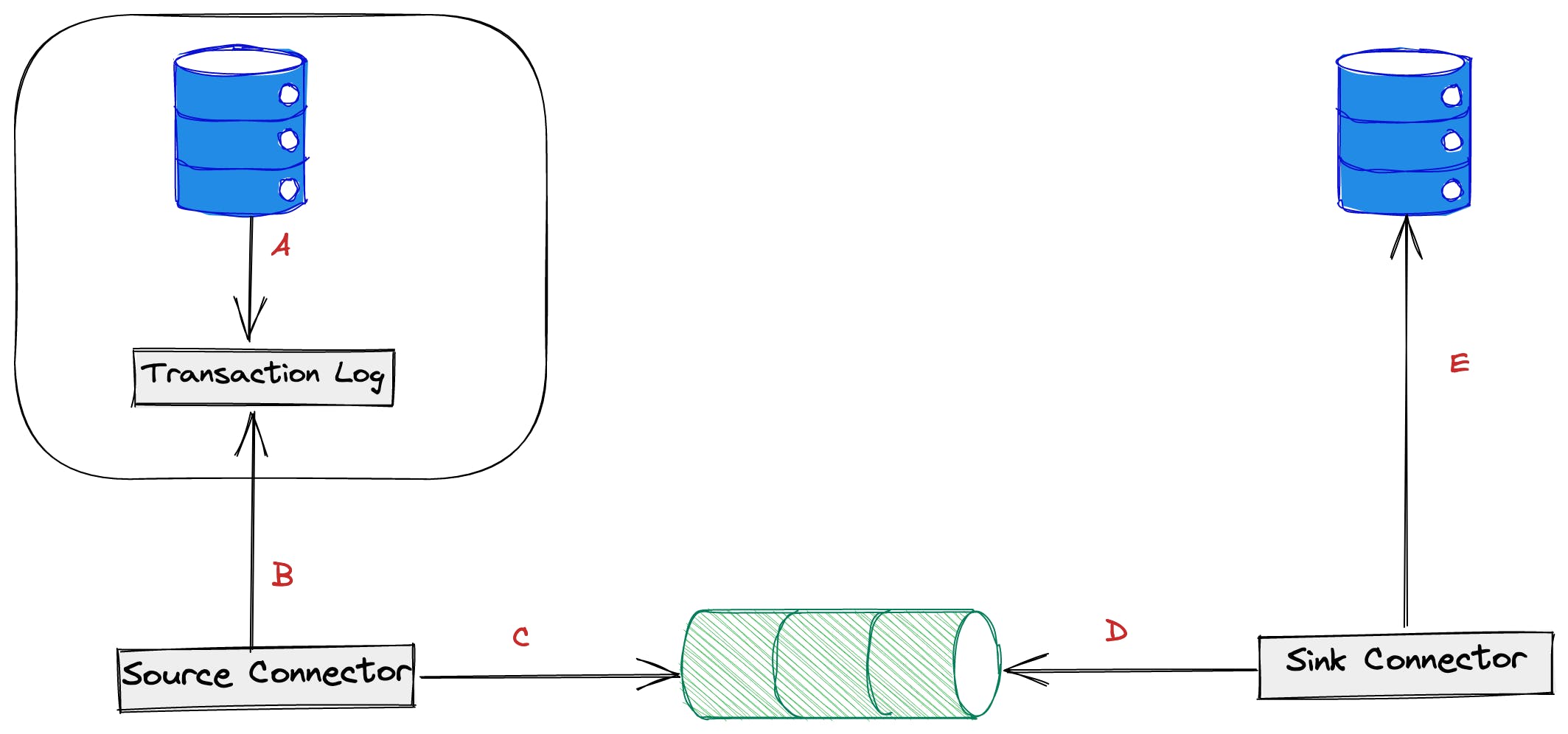
A: Databases maintain transactional log where it writes all DDL & DML queries. MySQL maintains binlog and PostgreSQL maintains WAL (write-ahead logs).
B & C: The source connector connects to the database and reads the transaction logs. It then prepares an in-memory structure of the change and writes to the message broker. Generally, CDC systems maintain a single schema for the change so that different database connectors transform the data into it.
D & E: The sink connector connects to the message broker, reads the data, and writes the change to the target database.
Use-cases of CDC
Let's think about different use cases of CDC in software engineering.
OLAP (online analytical processing) systems use CDC to migrate data from transactional databases to analytical databases.
OLTP (online transactional processing) systems can also use CDC as an event bus to replicate data in a different data store. For example, from MySQL to Elasticsearch.
One of the popular and widely-used systems is debezium. In this blog post, we will discuss how to set up debezium and how it works internally.
Debezium
Debezium works on top of kafka connect. Kafka Connect is a framework for streaming data between multiple systems. When deployed, it provides REST APIs to manage connectors. There are two connectors, the source, and the sink. As we saw from the above diagram, the source connector reads the source database and writes the data to the kafka topics. The sink connectors read from those kafka topics and write to the target database. Debezium is built using the kafka connect framework. It comes with connectors for different databases.
Debezium can only be installed through docker. The installation is very easy. Just pull the image from the registry and run it. More instructions are given here. Once deployed, the debezium server will be running on port 8083 by default. We can hit its REST API to create connectors.
# view connectors
curl -i -X GET localhost:8083/connectors
# create a connector
curl -i -X POST -H "Accept:application/json" -H "Content-Type:application/json" localhost:8083/connectors/ -d @mysql-connector.json
# delete a connector
curl -i -X DELETE localhost:8083/connectors/<connector name>
Debezium and MySQL
MySQL maintains a binary log (binlog) that writes all the schema changes and data changes in the same order as they happened. The debezium MySQL connector reads the binlog and produces change events for every schema and row-level change.
Create a MySQL User
In order for debezium to read binlog, it should have a user with specific permissions. Before we deploy our MySQL connector, let's create a user with the following commands.
CREATE USER 'user'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'password';
GRANT SELECT, RELOAD, SHOW DATABASES, LOCK TABLES, REPLICATION SLAVE, REPLICATION CLIENT ON *.* TO 'user' IDENTIFIED BY 'password';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Enable binlogs
The procedure for enabling binlogs in a self-hosted environment is easy. The instructions are given here. If you are using managed services like AWS, you can enable it from the console. Also, AWS RDS gives a few stored procedures to set this.
# show rds config
call mysql.rds_show_configuration;
# set binlog retention period
call mysql.rds_set_configuration('binlog retention hours', 96);
Deploy MySQL Connector
Before deploying a MySQL connector, we need to prepare the JSON.
{
"name": "debezium-connector1",
"config": {
"connector.class": "io.debezium.connector.mysql.MySqlConnector",
"database.hostname": "localhost",
"database.port": "3306",
"database.user": "debezium",
"database.password": "abc123",
"database.server.id": "130",
"topic.prefix": "prod-debezium",
"database.include.list": "mydatabase",
"table.include.list": "mydatabase.users,mydatabase.orders",
"snapshot.mode": "initial",
"schema.history.internal.kafka.bootstrap.servers": "localhost:9092,locahost:9093,localhost:9094",
"schema.history.internal.kafka.topic": "dbhistory.debezium",
"provide.transaction.metadata": "true",
"topic.creation.default.replication.factor": 2,
"topic.creation.default.partitions": 10,
"database.history.skip.unparseable.ddl": "true",
"event.processing.failure.handling.mode": "warn",
"snapshot.lock.timeout.ms": 180000,
}
}
Let's try to understand the meaning of each configuration. I skip self-explanatory configs and mention only the important ones.
connector.class - This is the path to the connector in the debezium code. When this connector is deployed, that particular class will run and process the data. So, it is important to give this config correctly.
database.server.id - The unique identifier of the connector. This differentiates the other MySQL connector.
topic.prefix - In older versions, it used to be database.server.name . This provides a namespace for the current instance of the connector. Debezium creates kafka topics by appending this prefix with the table name i.e. <topic.prefix>.<table_name>. This should be unique for a connector else debezium assumes it is an existing connector and tries to resume from where it stopped.
Database History Topic
A client connects to the database and reads its current schema. But the schema can change anytime. So, the debezium connector cannot just read the current schema because it may be processing the older change events from the database. It needs to correlate the current change with the exact schema. So, It needs to store the schema changes somewhere.
We know that MySQL emits the schema changes along with the row level changes to the binlog. Debezium reads the DDL statements, prepares an in-memory representation of the table, and also stores them in a separate topic along with the binlog position. This topic is called database history topic. It is configured with schema.history.internal.kafka.topic .
When the connector restarts, it reads the schema history topic and starts rebuilding the in-memory representation of each table, and resumes reading the binlog where it left off. The debezium connector emits the schema along with the row-level change so that the consumer systems can rebuild the whole table.
A very important note about the history topic is it is only for debezium internal use and it should not be partitioned. Meaning, it should have a partition of only one. Why? because in kafka the ordering of messages is guaranteed only at the partition level, not at the topic level. So, if it is partitioned, then the order of schema changes will be mixed which leads to chaos.
This is how the data from the schema history topic looks
{
"source" : {
"server" : "prod-debezium"
},
"position" : {
"transaction_id" : null,
"ts_sec" : 1674648853,
"file" : "mysql-bin-changelog.106869",
"pos" : 69735280,
"server_id" : 1229362390
},
"databaseName" : "licious",
"ddl" : "CREATE TABLE `user_groups` (\n\t`id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,\n\t`user_id` bigint(20),\n\t`customer_key` varchar(25) NOT NULL,\n\tCONSTRAINT FOREIGN KEY `fk_user_id` (user_id) REFERENCES `users`(id) ON DELETE CASCADE,\n\tCONSTRAINT UNIQUE KEY `unique_user_group_id` (user_id, customer_key)\n) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1",
"tableChanges" : [ ]
}
Schema Change Topic
As the schema history topic is for the internal use of debezium, it provides a schema change topic where external consumers can consume the schema change events. The topic name can be configured with topic.prefix (earlier database.server.name)
Snapshots
Debezium stores the snapshots of the database to provide high fault tolerance. In order to perform a snapshot, the connector first tries to get the global read lock that blocks the writes by the other clients and then reads the schema of all the tables and releases the lock. Acquiring a lock is very important because it helps in maintaining consistency as it blocks writes during that period. In case the global read lock is not possible, then it acquires table-level locks. More about it here.
There are different modes of snapshots. It can be configured with snapshot.mode . The most used modes are
initial used when you need the schema changes and the row level changes from the beginning. Schema changes are written to schema history and schema change topics and the data changes are written to <topic.prefix>.<table_name> .
schema_only takes the snapshot of only schema. This is useful if you don't want the entire data of the tables instead you only need the data from the moment you deployed. This mode is used if your tables contain dynamic data in an OLTP system.
when_needed takes the snapshot whenever it's necessary i.e. when the binlogs are deleted or the schema history topic is deleted etc...
Troubleshooting Debezium
The MySQL server is not configured to use a ROW binlog_format, which is required for this connector to work properly
io.debezium.DebeziumException: The MySQL server is not
configured to use a ROW binlog_format, which is required for this
connector to work properly. Change the MySQL configuration to use a
binlog_format=ROW and restart the connector. at
io.debezium.connector.mysql.MySqlConnectorTask.validateBinlogConfiguration(MySqlConnectorTask.java:262) at
io.debezium.connector.mysql.MySqlConnectorTask.start(MySqlConnectorTask.java:86) at
io.debezium.connector.common.BaseSourceTask.start(BaseSourceTask.java:130) at
org.apache.kafka.connect.runtime.WorkerSourceTask.execute(WorkerSourceTask.java:232) at
Change the MySQL configuration either through /etc/mysql.cnf or by executing the below command in the MySQL shell.
SET GLOBAL binlog_format = 'ROW';
Refer - MySQL Documentation
Database history topic retention.ms should be ‘-1’ or greater than 5 years
2022-01-06 13:08:55,904 WARN || Database history topic
'dbhistory.dev-jigyasa-licious' option 'retention.ms' should be '-1' or greater than '157680000000' (5 years)
but is '604800000' [io.debezium.relational.history.KafkaDatabaseHistory]
Set the retention.ms property of database history topic to -1 via kafka CLI.
The connector is trying to read binlog but this is no longer available on the server.
2022-01-06 13:08:56,405 ERROR ||
WorkerSourceTask{id=jigyasa-mysql-connector-licious-2-0} Task threw an uncaught and unrecoverable exception.
Task is being killed and will not recover until manually restarted
[org.apache.kafka.connect.runtime.WorkerTask] io.debezium.DebeziumException:
The connector is trying to read binlog starting at SourceInfo [currentGtid=null,
currentBinlogFilename=mysql-bin-changelog.032256, currentBinlogPosition=53270, currentRowNumber=0,
serverId=0, sourceTime=null, threadId=-1, currentQuery=null, tableIds=[], databaseName=null],
but this is no longer available on the server. Reconfigure the connector to use a snapshot when needed.
2022-01-06 13:08:56,405 INFO || Connector requires binlog file
'mysql-bin-changelog.032256', but MySQL only has mysql-bin-changelog.032918, mysql-bin-changelog.032919,
mysql-bin-changelog.032920 [io.debezium.connector.mysql.MySqlConnectorTask]
Extend the binlog retention time using the commands mentioned above.
Delete the connector and re-deploy it again using REST API.
Could not find the first log file name in the binary log index file Error code: 1236; SQLSTATE: HY000.
org.apache.kafka.connect.errors.ConnectException: An exception occurred in the change event producer. This connector will be stopped.
at io.debezium.pipeline.ErrorHandler.setProducerThrowable(ErrorHandler.java:42)
at io.debezium.connector.mysql.MySqlStreamingChangeEventSource$ReaderThreadLifecycleListener.onCommunicationFailure(MySqlStreamingChangeEventSource.java:1217)
at com.github.shyiko.mysql.binlog.BinaryLogClient.listenForEventPackets(BinaryLogClient.java:980)
at com.github.shyiko.mysql.binlog.BinaryLogClient.connect(BinaryLogClient.java:599)
at com.github.shyiko.mysql.binlog.BinaryLogClient$7.run(BinaryLogClient.java:857)
at java.base/java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:829)
Caused by: io.debezium.DebeziumException: Could not find first log file name in binary log index file Error code: 1236; SQLSTATE: HY000.
at io.debezium.connector.mysql.MySqlStreamingChangeEventSource.wrap(MySqlStreamingChangeEventSource.java:1172)
... 5 more
Caused by: com.github.shyiko.mysql.binlog.network.ServerException: Could not find first log file name in binary log index file
at com.github.shyiko.mysql.binlog.BinaryLogClient.listenForEventPackets(BinaryLogClient.java:944)
... 3 more
This generally happens if you had upgraded MySQL, and cleaned up the binlogs. Delete the connector and re-deploy it again using REST API.
io.debezium.DebeziumException: Failed to read next byte from position 1640249837
org.apache.kafka.connect.errors.ConnectException: An exception occurred in the change event producer. This connector will be stopped.
at io.debezium.pipeline.ErrorHandler.setProducerThrowable(ErrorHandler.java:42)
at io.debezium.connector.mysql.MySqlStreamingChangeEventSource$ReaderThreadLifecycleListener.onCommunicationFailure(MySqlStreamingChangeEventSource.java:1217)
at com.github.shyiko.mysql.binlog.BinaryLogClient.listenForEventPackets(BinaryLogClient.java:980)
at com.github.shyiko.mysql.binlog.BinaryLogClient.connect(BinaryLogClient.java:599)
at com.github.shyiko.mysql.binlog.BinaryLogClient$7.run(BinaryLogClient.java:857)
at java.base/java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:829)
Caused by: io.debezium.DebeziumException: Failed to read next byte from position 1640249837
at io.debezium.connector.mysql.MySqlStreamingChangeEventSource.wrap(MySqlStreamingChangeEventSource.java:1172)
... 5 more
Caused by: java.io.EOFException: Failed to read next byte from position 1640249837
at com.github.shyiko.mysql.binlog.io.ByteArrayInputStream.read(ByteArrayInputStream.java:213)
at com.github.shyiko.mysql.binlog.io.ByteArrayInputStream.readInteger(ByteArrayInputStream.java:52)
at com.github.shyiko.mysql.binlog.event.deserialization.EventHeaderV4Deserializer.deserialize(EventHeaderV4Deserializer.java:35)
at com.github.shyiko.mysql.binlog.event.deserialization.EventHeaderV4Deserializer.deserialize(EventHeaderV4Deserializer.java:27)
at com.github.shyiko.mysql.binlog.event.deserialization.EventDeserializer.nextEvent(EventDeserializer.java:221)
at io.debezium.connector.mysql.MySqlStreamingChangeEventSource$1.nextEvent(MySqlStreamingChangeEventSource.java:230)
at com.github.shyiko.mysql.binlog.BinaryLogClient.listenForEventPackets(BinaryLogClient.java:952)
... 3 more
This happens if the binlog contains any special character that the connector is not able to process. One way to resolve this is to set event.processing.failure.handling.mode to warn in the connector configuration.
MySQLTransactionRollbackException: Lock wait timeout exceeded; try restarting transaction
org.apache.kafka.connect.errors.ConnectException:An exception occurred in the change event producer. This connector will be
stopped.
at
io.debezium.pipeline.ErrorHandler.setProducerThrowable(ErrorHandler.java:42)
at
io.debezium.pipeline.ChangeEventSourceCoordinator.lambda$start$0(ChangeEventSourceCoordinator.java:115)
at
java.base/java.util.concurrent.Executors$RunnableAdapter.call(Executors.java:515)
at java.base/java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.run(FutureTask.java:264)
at
java.base/java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1128)
at
java.base/java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:628)
at java.base/java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:829)
Caused by:
io.debezium.DebeziumException: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.exceptions.MySQLTransactionRollbackException: Lock wait
timeout exceeded; try restarting transaction
at
io.debezium.pipeline.source.AbstractSnapshotChangeEventSource.execute(AbstractSnapshotChangeEventSource.java:85)
at
io.debezium.pipeline.ChangeEventSourceCoordinator.doSnapshot(ChangeEventSourceCoordinator.java:153)
at
This happens when the debezium connector failed to get the global read lock or table level lock.
Increase the
snapshot.lock.timeout.msto 10-15 minutes and re-deploy the connector so that the debezium connector waits for some more time to acquire the lock.If the above solution did not help, it means that the database is busy. Simply, kill all those clients and re-deploy the connector.
show open tables where in_use>0;
show full processlist;
kill <pid>;